ECOTRON: How to minimize the ecological footprint for functional electronics?
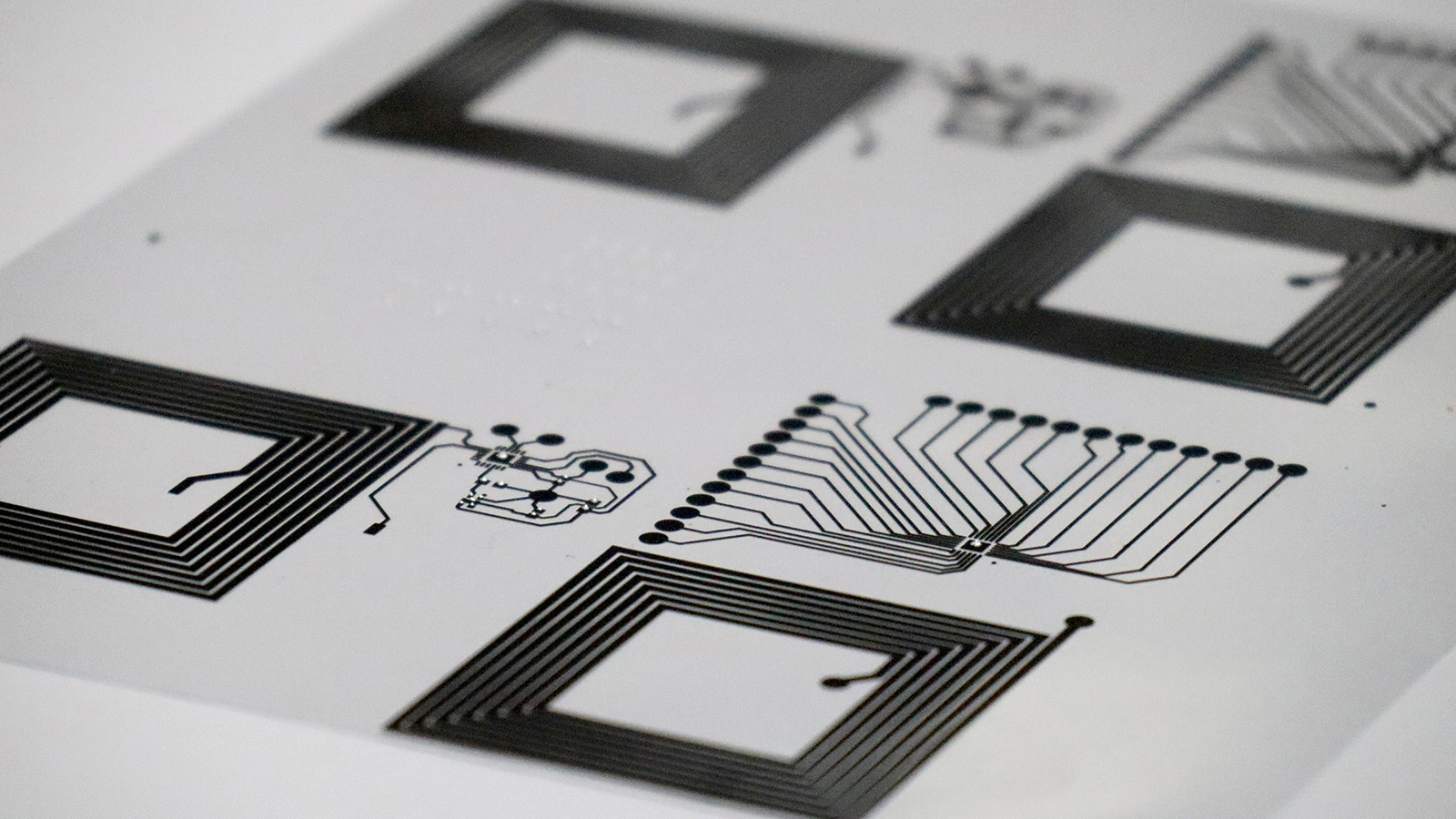
The aim of the ECOTRON project is to reduce the environmental impact of printed electronic devices by reducing the use of materials obtained from non-renewable sources and their size, as well as by improving the recycling process.
Context
The growing demand for real-time data and information has led to the integration of electronic functionalities into everyday objects. Consumer electronics, healthcare, wearable electronics, the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart packaging are some examples.
Nowadays, electronic devices are widely used for all applications and have a wide variety of components that have a high environmental impact in their manufacture, use and end of life.
Printed electronics, due to its manufacturing process, have a lower impact. However, it still uses compounds extracted from non-renewable sources and electronic components, such as ICs, resistors and capacitorsthat condition their subsequent recycling.
Summary and objectives
The aim of the ECOTRON project is to improve the recyclability of printed electronic devices through a multidisciplinary approach including the introduction of bio-based materials, innovative printing processes and device and module disassembly technologies. In addition, industrially scalable recycling standards and technologies will be developed.
These new technologies will be validated within the project through the creation of 4 demonstrators in different industrial environments.
- printed lighting panel for offices
- smart sensorised packaging for temperature control
- renewable in-body drug delivery system for the healthcare sector
- monitoring systems for wearable electronics
The project defines several specific objectives:
- Development of new technologies through product life cycle studies where critical impacts will be analysed and will allow the eco-design of products to improve their circularity. and establishment of requirements for the eco-design of printed electronics. It will include restrictions for material waste streams, dismantling methods, the application of reversible interconnection technology and standardisation requirements that will be based on ISO 14006:2020.
- Improving recyclability through dismantling or separation processes, such as reversible connections of electronic components to facilitate their separation at end-of-life.
- Creation of a plan for a pilot plant for the recycling of printed electronics. The printed electronic products, the definition of waste streams (liquid, solid and/or gaseous), dismantling methods at product and component level and specific end-use requirements will be defined. Based on these data, a process plan will be developed.
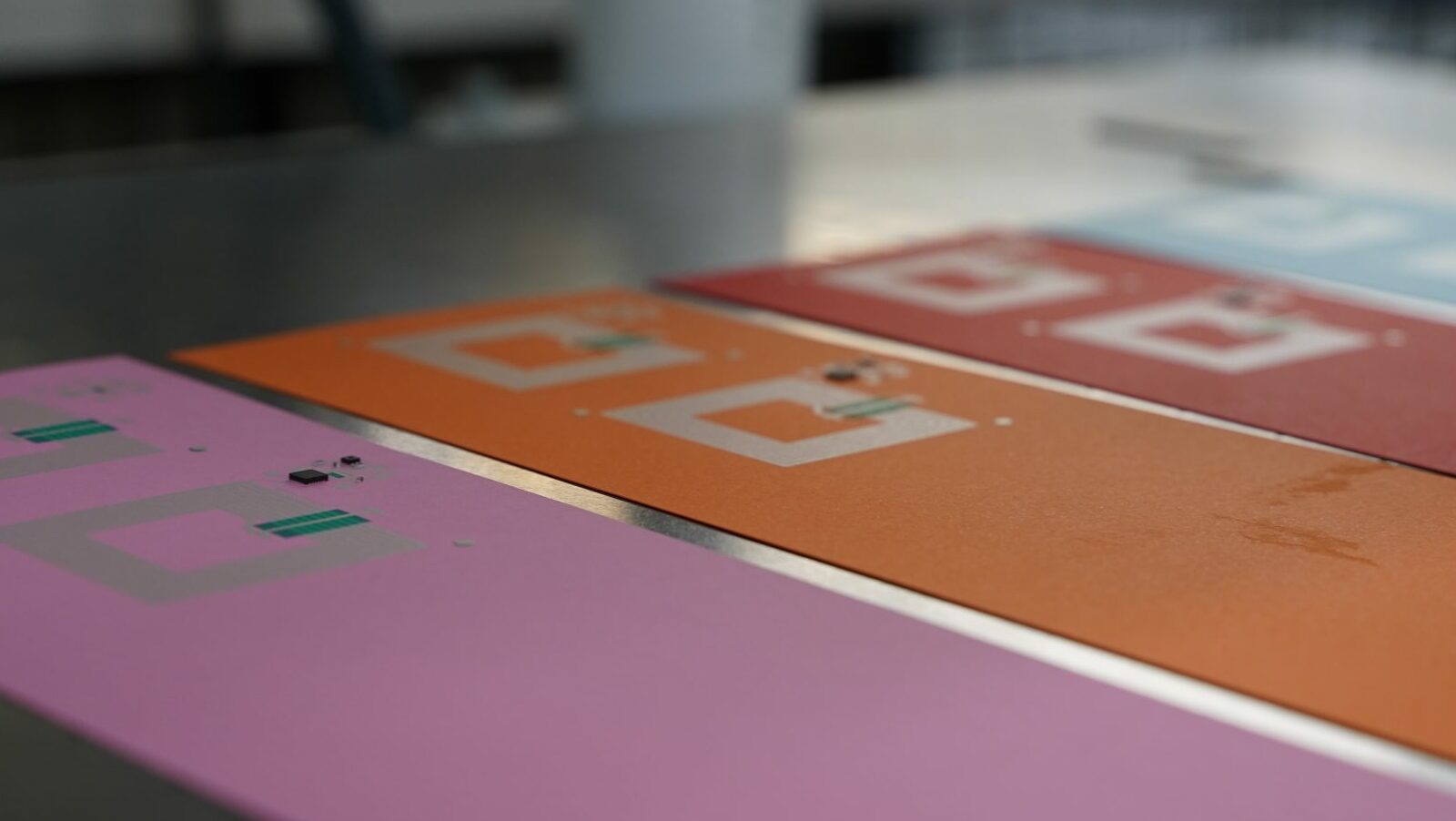
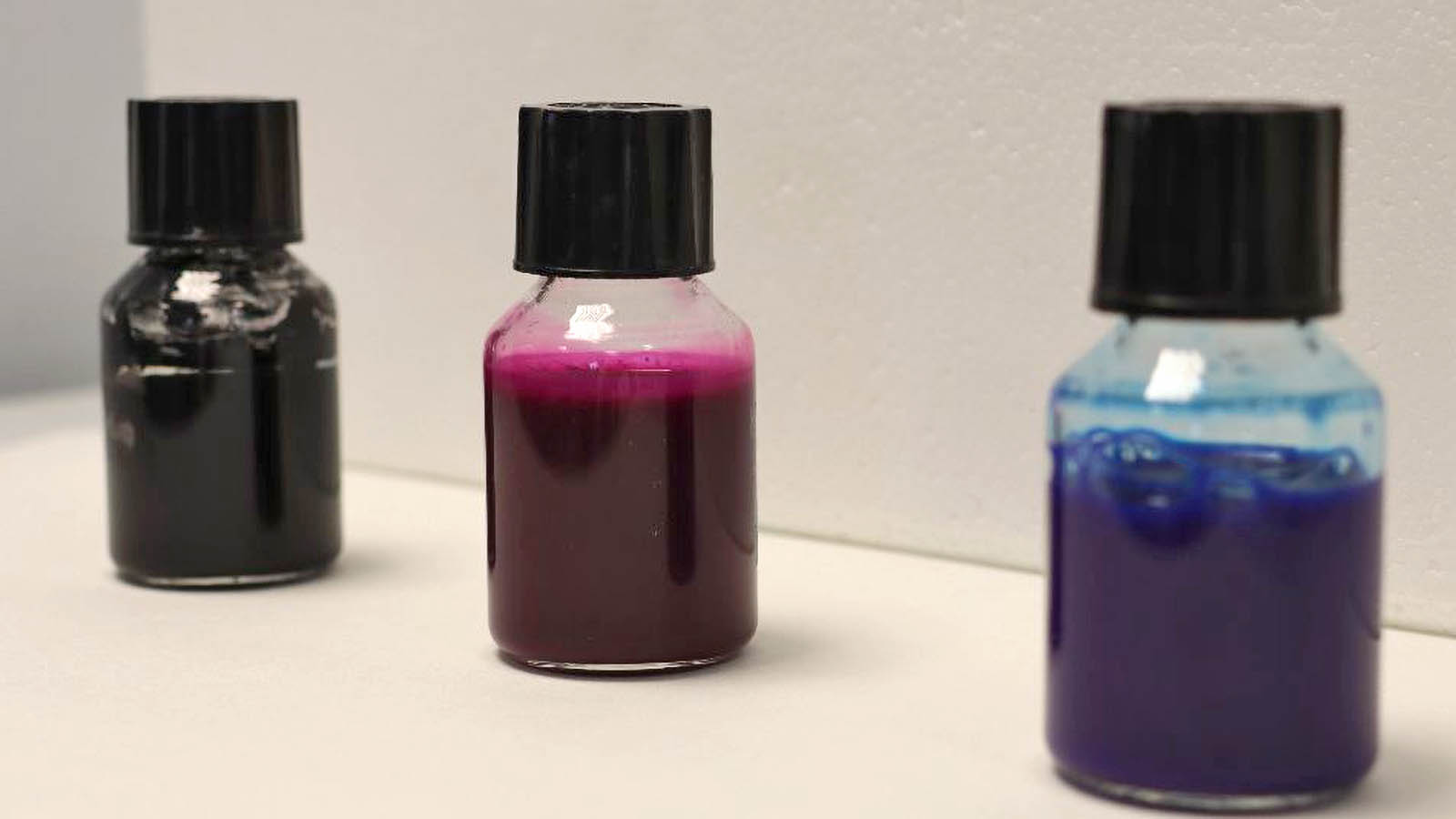
- Development of bio-based and compostable conductive substrates and inks, in line with reducing the use of non-renewable sources.
- Printing process (high resolution reverse offset printing) that will minimise the size/structure and carbon footprint of the electronics.
Consortium
The ECOTRON consortium brings together 11 partners from 8 countries, including 4 non-profit research organisations and associations, 2 SMEs, 4 larger companies and 1 university.
- NEDERLANDSE ORGANISATIE VOOR TOEGEPAST NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK TNO (TNO) (Netherlands) (Coordinator).
- TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT OY (VTT) (Finland).
- COMMISSARIAT À L’ÉNERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ÉNERGIES ALTERNATIVES (CEA (France).
- INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO DEL EMBALAJE, TRANSPORTE Y LOGÍSTICA (ITENE) (Spain).
- SIGNIFY NETHERLANDS BV (SIG) (Netherlands).
- BECTON DICKINSON FRANCE SAS (BD France) (France).
- JANSSEN PHARMACEUTICA NV (JANSSEN) (Belgium).
- TÉCNICAS REUNIDAS SA (TRSA) (Spain).
- POLITECNICO DI MILANO (POLIMI) (Italy).
- POLAR ELECTRO OY (POL) (Finland).
- AMIRES SRO (AMIRES SRO) (Czechia).
ITENE’s role
ITENE will lead the environmental assessment using life cycle analysis tools of current products and those to be developed in the project to determine the impact of the traditional manufacturing of electronic devices and to propose its reduction through printed electronics. In addition, the compostability of the different components and/or prototypes will be evaluated.
Moreover, ITENE will work on the development of bio-based conductive inks that can be separated from the support where they are printed and will facilitate the collection of the metallic particles that are part of their formulation. The development of carbon-based compostable conductive inks is also envisaged.
Together with other partners, it will evaluate the concepts developed in the test vehicle, the implementation of circular manufacturing, the execution of innovative processes and bio-based materials in different sectors and the development of pilot tests for the recycling of printed electronics products and a novel disassembly technique.




