Innovative Packaging trends to avoid Food Loss and facilitate waste reduction
Considering packaging waste and EUROSTAT data, the amount produced is approximately 77 million tonnes per year. Packed food waste has the disadvantage of including together organic and inorganic fractions that cannot be currently separated and are, therefore, sent to landfill. The inorganic fraction, represented mostly by packaging, can even reach up to 20% of the unit, and it is designed and produced for a single use, with really short lifetime periods. Several actions are being carried out for promoting reuse and recycling, involving companies, national and local authorities as well as citizens.

Active Packaging
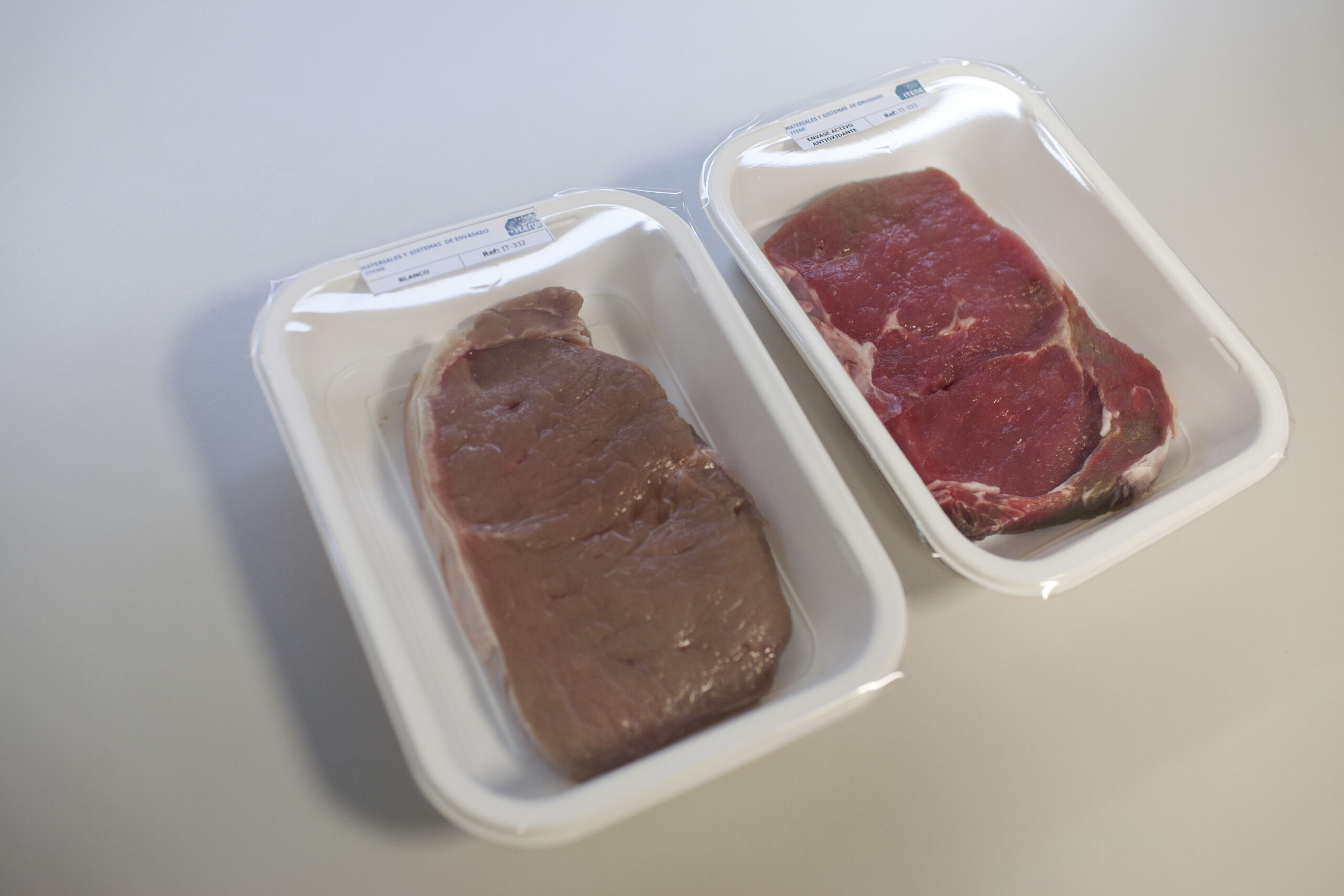
One of the new R&D trends to solve this issue is the development of Active Packaging technologies, able to extend food shelf life even twice as much as conventional packaging does. These innovative solutions avoid food losses not only in households but also in the industry and commercial sectors. Thanks
to these reductions, active packaging contributes to a smarter management of world limited food resources.
Antimicrobial, antifungal, oxygen, CO2 release are just a few examples of what these agents incorporated in the packaging material release to the product, thus keeping a high quality performance during a longer time and thus, increasing the products´ shelf life and avoiding tons of food waste.

Smart Packaging
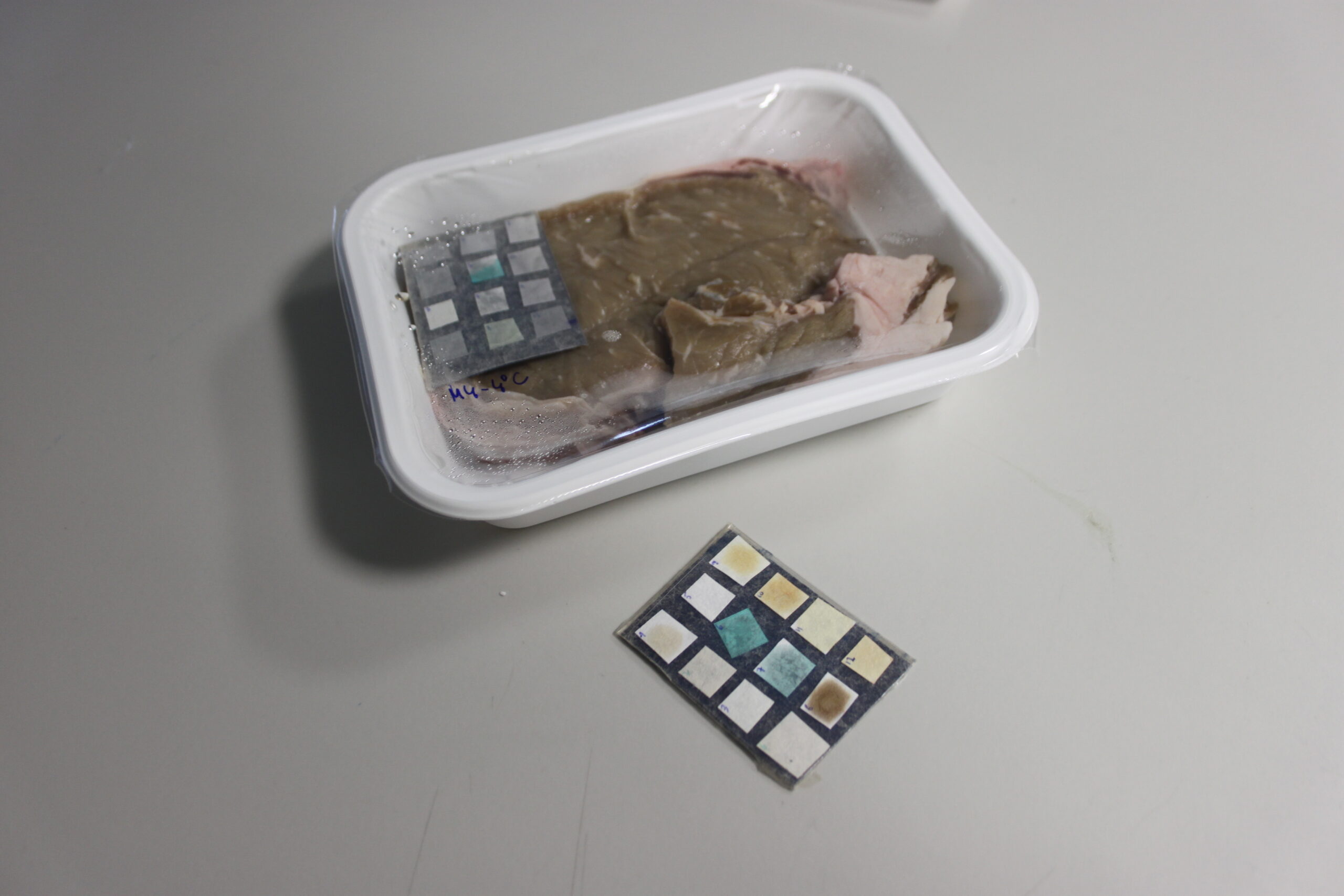
Another trend comes from the development of Smart Packaging technologies able to provide valuable information (i.e. not only an uncertain expiration date) to the user and consumer about current product spoilage, thus helping them to make decisions. Colorimetric indicators (labels) are incorporated onto packaging and change their colour to show product freshness level, product exposure to unsuitable temperatures, etc. So these smart indicators give reliable information about foodstuffs to avoid unnecessary food loss along the whole supply chain. I.e. A freshness indicator developed by ITENE applied to a packaging solution for monitoring chicken meat freshness has been developed through the SENSOPACK project. This technology will inform in an easy way about the real shelf life of packed fresh chicken meat. The indicator uses ink that is formulated using a reactive indicating compound, instead of common dyes or pigments. The indicator colour is related to the degree of freshness of the meat product. It encourages product traceability as well as other critical distribution parameters such as temperature abuse, losses of freshness, especially in food packaged products like one able to inform about the food quality or about the real shelf life of each individual product according to their microbial loads and degree of freshness, in order to print longer shelf life on the products.

Food waste
To describing another featured trend, we can highlight Smart recycling systems, which are able to separate food fractions from packaging in order to make them suitable for a wide range of valorising processes. Food products are usually packed for preserving their properties during the stages of transport, distribution and commercialization. Therefore, food waste not only includes organic fractions but also inorganic components such as plastics, metals, paper or wood. Separating both the inorganic and the organic fraction of food waste currently reveals technical limitations that need to be overcome. Recycling systems able to separate and properly recycle food waste will mean an important reduction of food waste sent to landfill on one hand, and to make it available for new uses, for example, in cattle feed production, on another.
ITENE participates in relevant European projects developing innovative technologies for packaged and unpackaged food waste. I.e. EU project LIFE FOODWASTE TREATMENT collaborating with BiogasFuel, FIAB and IMABE.
An advanced and efficient separation and post-treatment technology, which will allow giving packed and unpacked food, waste different management options away from current incineration and landfill disposal.
Packaging Optimization

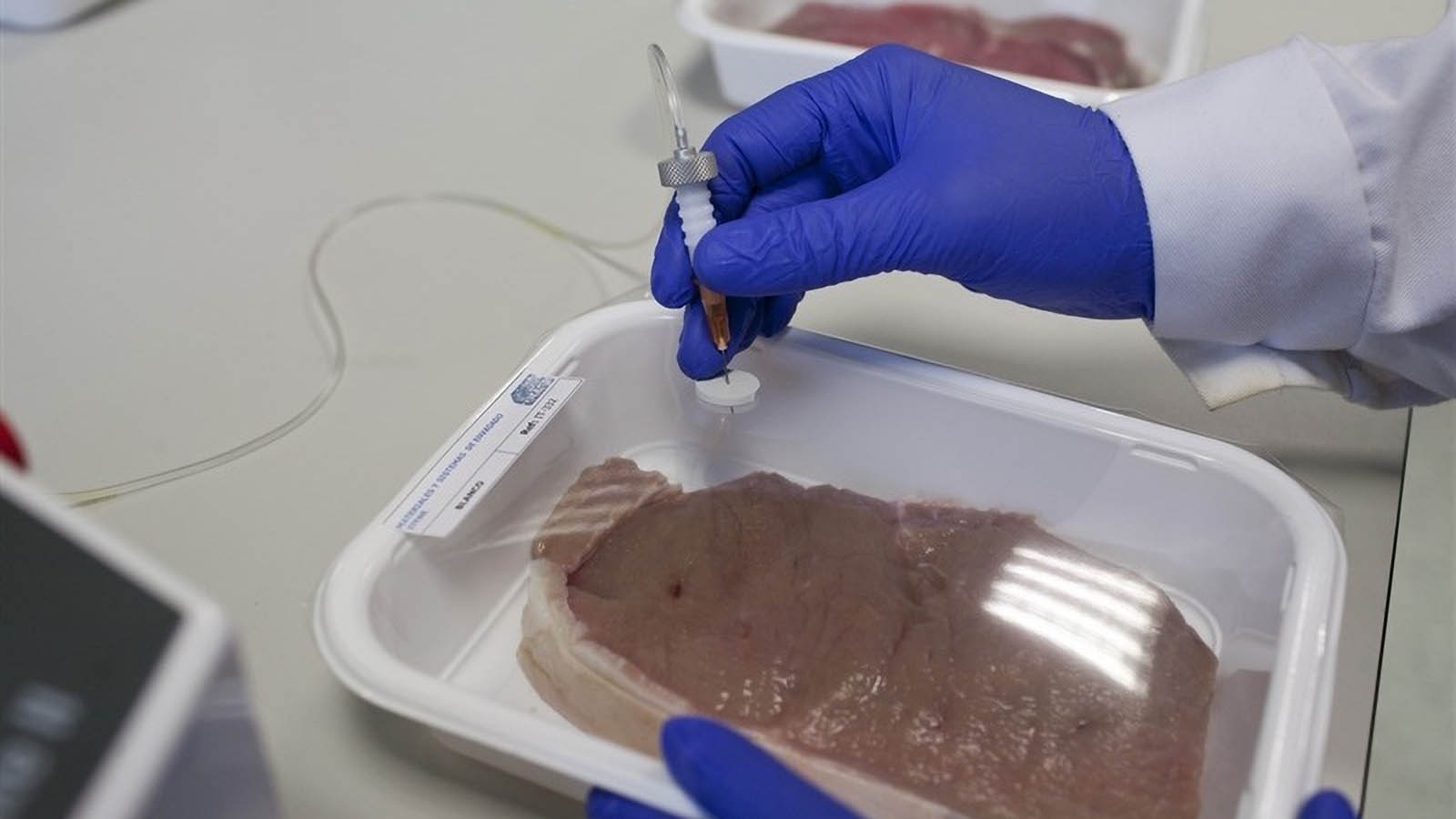
ITENE also designed trials to obtain data through the use of sensors and to determine the behaviour of materials and packaging to temperature, pressure, humidity, etc.
Finally, different design options are implemented in real environments achieving a food losses reduction of about 10-40%.
Sustainability

For example, according to the main Directives on Waste and Packaging Waste, prevention is the first action to be considered. The best waste is the one that is not generated.
Conventional materials like plastics, paper, and glass, among others, have reached incredible reduction figures (among the 20-40%) in some applications. Research in new manufacturing packaging technologies has made possible these achievements that were impossible in the past. New additives coming from the nature may help to keep or even overcome mechanical barrier and other interesting properties by being added to the packaging material.

As a conclusion, different options for reducing packaging losses must always be cost-effective, environmental compatible and accepted by the final customers. These three elements are essential to get solutions placed in the market that could help preventing the potential food losses.